FLOW-3D HYDRO 2024R1 full cracked release
$ 170.00
FLOW-3D HYDRO serves as a comprehensive 3D computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling solution tailored for the civil and environmental engineering sectors. Utilizing the advanced FLOW-3D solver engine, this innovative platform equips engineers and water resource professionals with superior simulation tools to address contemporary challenges in water management and conservation. The software features a precise free surface modeling capability, enhanced by various additional functionalities such as air entrainment, sediment transport and scour, tailings flow analysis, and hybrid 2D/3D modeling. Designed to operate across diverse computing environments, from personal laptops to high-performance computing clusters, FLOW-3D HYDRO boasts an intuitive, water-centric user interface, ready-to-use simulation templates, and extensive training and support resources, making it accessible for both newcomers to 3D CFD and seasoned numerical modeling practitioners…
Description
An exciting new development in FLOW-3D HYDRO 2024R1 is the introduction of a Site coordinate system (sometimes called a local or project coordinate system) that facilitates working with geographic coordinate systems by allowing objects such as topography and bathymetry to be defined in a geographic coordinate system (e.g., UTM) while other objects are defined in a convenient local coordinate system (e.g., BIM coordinates). This new capability reduces the time, effort, and risk associated with manual coordinate transformations during the model setup with a clear, simple interface for setting the Site coordinate system, as well as an option to simply read it from a Revit shared coordinate file.

A second development for FLOW-3D HYDRO is to include LandXML and the triangulated raster surfaces into the EXODUS II-based output files. This makes the full topography/bathymetry available when postprocessing, making it easier to convey results to your audience in a way that focuses on the story rather than the modeling details.

What’s New in FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R2
New results file format
We introduced an all-new results file format based on the EXODUS II format, enabling faster postprocessing in FLOW-3D HYDRO and FLOW-3D POST 2023R2. This new file format significantly reduces the time spent on postprocessing tasks for large, complex simulations (up to 5x on average!) while improving connectivity with other visualization tools.
Users now have the choice to write Selected data in either flsgrf, EXODUS II, or both flsgrf and EXODUS II file formats. The new EXODUS II file format utilizes finite element meshes for each object, which allows users to also open FLOW-3D HYDRO results with other compatible postprocessors and FEA codes. With the new workflow, users can visualize large, complex cases quickly and extract auxiliary information using arbitrary slicing, volume renders, and statistics.
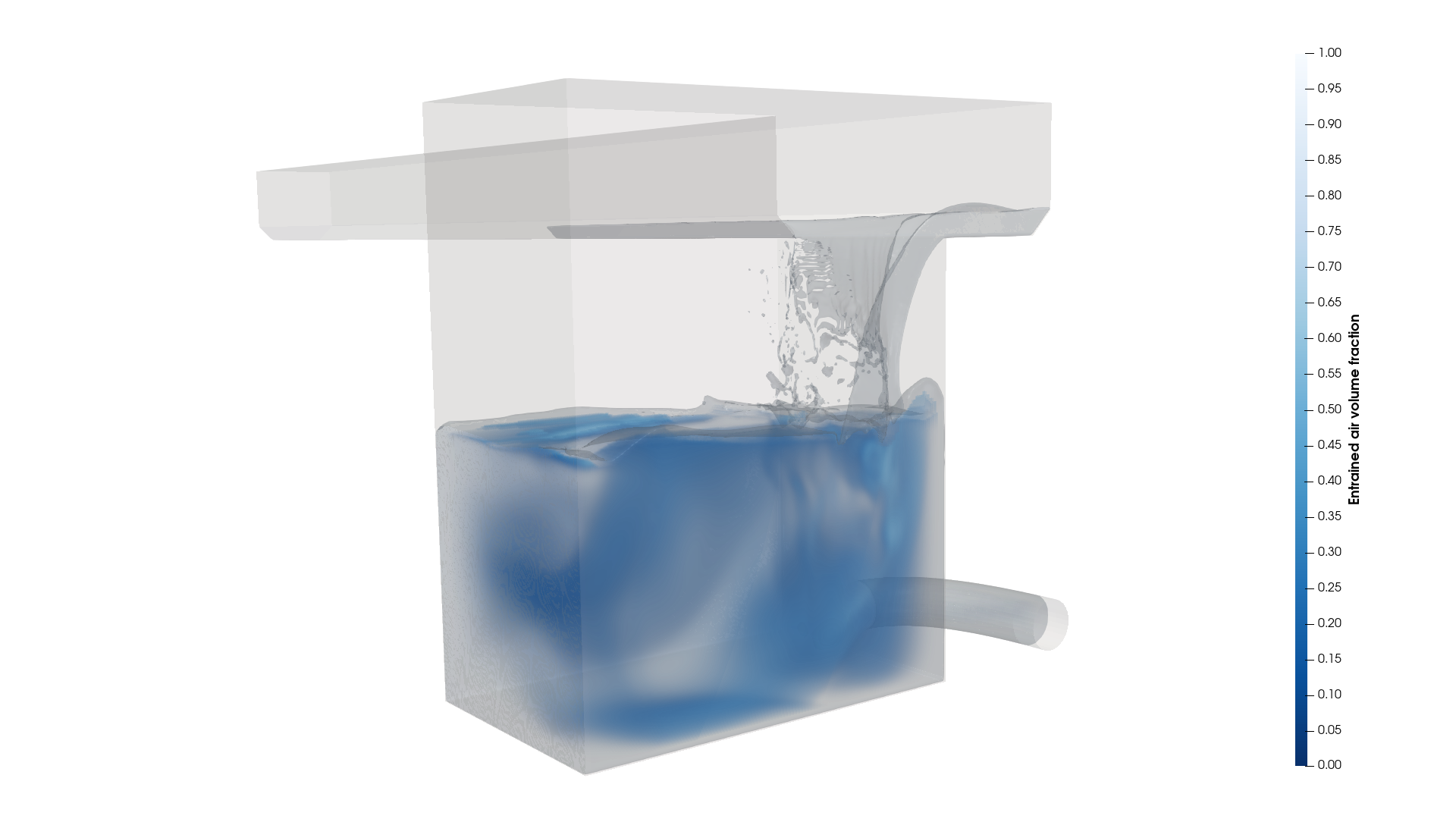
The new results file format boasts a remarkable speed-up in visualization workflows compared to flsgrf without sacrificing the performance of the hydr3d solver. This exciting new development provides a seamless simulation experience with improved speed and flexibility in results analysis.
Turbulence model improvements
FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R2 brings a major improvement to the dynamic mixing length calculation for two-equation (RANS) turbulence models. In certain limiting cases such as near-laminar flow regimes, the code-computed limiter could in previous versions sometimes be overpredicted, forcing the user to manually input a specific mixing length.
The new dynamic mixing length calculation better accounts for the turbulent length and time scales in these situations, and users can now apply the dynamic model to a wider range of flows instead of setting a fixed (physics-based) mixing length.

Hydrostatic pressure initialization
It is often necessary for users to initialize hydrostatic pressure in pre-defined fluid regions. Previously in large, complex simulations, the hydrostatic pressure solver could sometimes be slow to converge. FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R2 brings a significant performance improvement to the hydrostatic solver, enabling it to converge up to ~6x faster during the preprocessing stage.
Expanded terrain representation support
GeoTIFF support
With the 2023R2 release, FLOW-3D HYDRO natively supports the GeoTIFF (.tif) file format for raster topography and bathymetry. Users can now directly import GeoTIFF files into the user interface.

LandXML support
In cases where survey data is non-uniform or raster surfaces do not have sufficient resolution, TIN surfaces offer an improved map of the topography via the LandXML (.xml) file format. FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R2 natively imports LandXML files.
Improved interactivity with raster files
Raster files often cover large topographic areas at high resolution, which can slow down the interactivity of the 3D representation in the user interface. Users can now control the quality of the 3D representation, greatly reducing the rendering time and significantly improving interactivity.
What’s New in FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R1
All products in the FLOW-3D software family received IT-related improvements in 2023R1. FLOW-3D HYDRO 2023R1 now supports Windows 11 and RHEL 8. Our Linux installer has been improved to report missing dependencies and it no longer requires root-level permissions, which makes installation easier and more secure. And for those of you who have automated your workflows, we added a command-line interface to our input file converter so that you can ensure your workflow is working with updated input files, even in scripted environments.
Shallow water turbulence models
Turbulence is a key aspect of water and environmental flow fields, especially so in regimes modeled with shallow water approximations. We enhanced our treatment of turbulence in our shallow water model to include three new turbulence models, the constant diffusivity, mixing length, and Smagorinsky models, to help reduce modeling risk and give better results.
What’s New in FLOW-3D HYDRO 2022R2
With the release of FLOW-3D HYDRO 2022R2, Flow Science has unified the workstation and HPC versions of FLOW-3D HYDRO to deliver a single solver engine capable of taking advantage of any type of hardware architecture, from single node CPU configurations to multi-node parallel high performance computing executions. Additional developments include improved entrained air functionalities, as well as boundary condition definition improvements for water and environmental applications.
Unified solver
We migrated our FLOW-3D products to a single, unified solver to run seamlessly on local workstations or on high performance computing hardware environments.
Many users run their models on laptops or local workstations, but in addition run larger models on high performance computing clusters. With the 2022R2 release, the unified solver allows users to exploit the same benefits of OpenMP/MPI hybrid parallelization from HPC solutions to run on workstations and laptops.
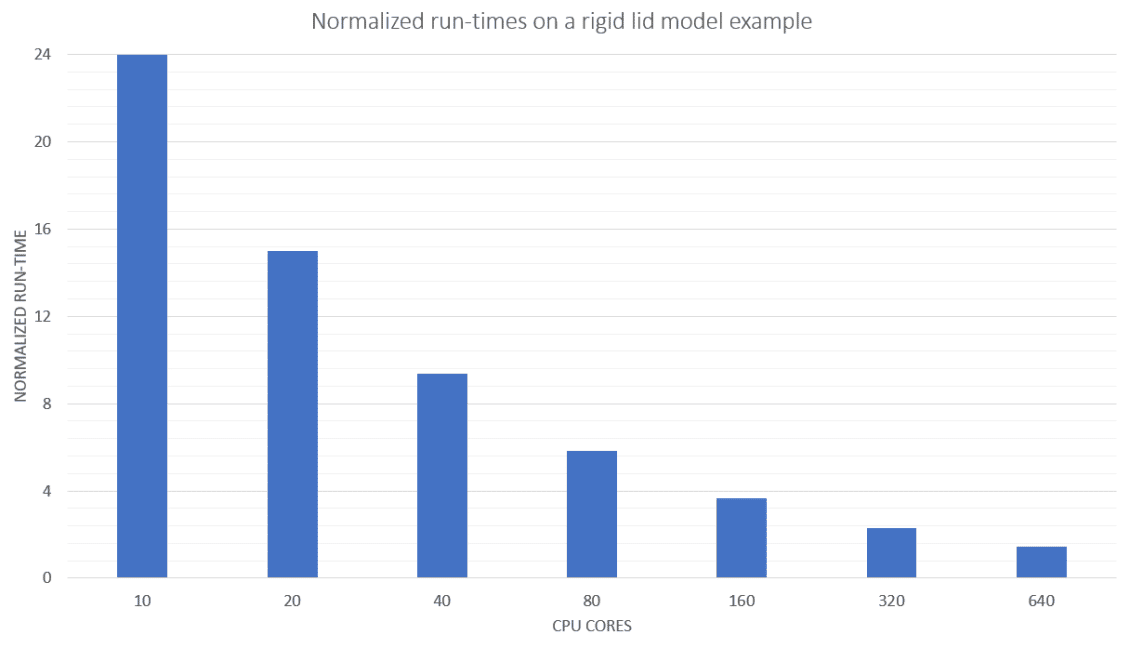
Multi socket workstations
Multi socket workstations are now very common and capable of running large simulations. With the new unified solver, users using this type of hardware will generally see performance gains from being able to run models taking advantage of OpenMP/MPI hybrid parallelization that used to be only available on HPC cluster configurations.
Low level routines improved vectorization and memory access
Performance gains on the order of 10% to 20% have been observed for most test cases, with some cases yielding run-time benefits in excess of 20%.
Refined volumetric convective stability limit
Time step stability limit is a major driver in model runtime, with 2022R2, a new time step stability limit, 3D convective stability limit, is available in the numerics widget. For models that are running and convection limited (cx, cy, or cz limits) the new option has shown typical speed-ups on the order of 30%.
Pressure solver pre-conditioner
In some cases, for challenging flow configurations, run times can be drawn out due to excessive pressure solver iterations. For those difficult cases, with 2022R2, when a model iterates too heavily, FLOW-3D automatically activates a new pre-conditioner to help with pressure convergence. Tests have improvements in runtime anywhere from 1.9 to 335 faster!
Log conformation tensor method for visco-elastic fluids
A new solver option for visco-elastic fluids is available to our users, and is particularly effective for high Weissenberg numbers.
FLOW-3D HYDRO boundary conditions refinements
Two improvements for water application boundary conditions are available in FLOW-3D HYDRO 2022R2. Shallow water volume flow rate boundary conditions have been improved to yield more realistic, spatially-varying velocity profiles so users can reduce the domain size without losing accuracy. For natural inlet boundary conditions, the response to transient conditions can be improved with the use of the rating curve relaxation time option.
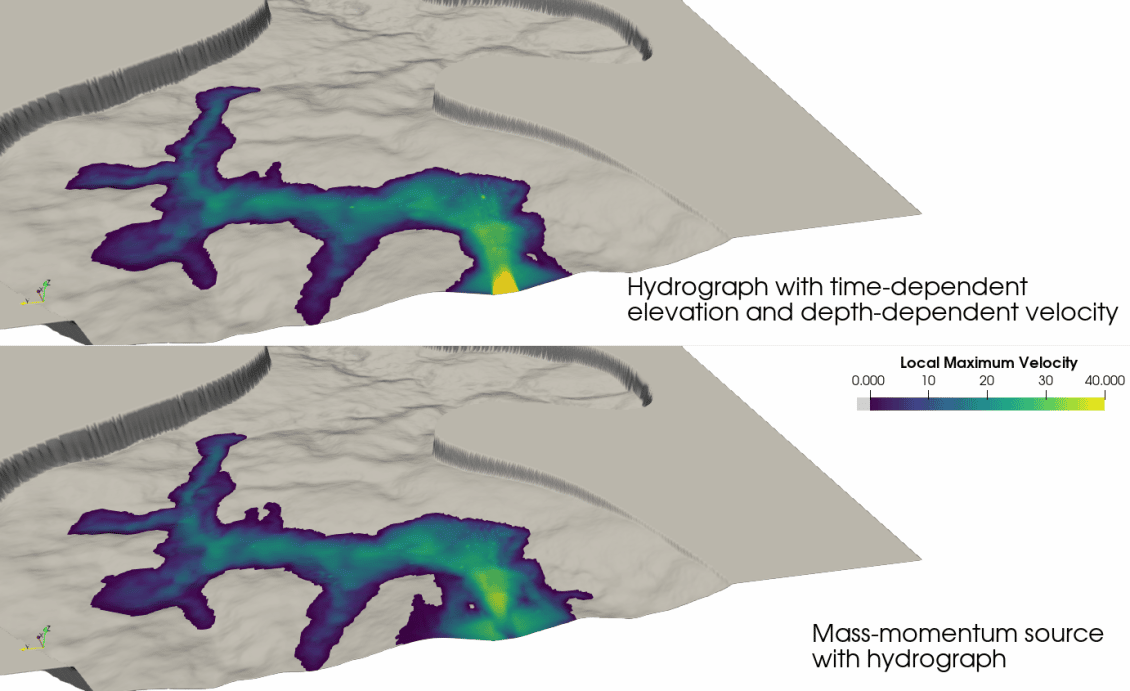
Improved entrained air functionalities
For diffusers and similar bubble flow applications, mass sources can now be used to introduce air into the water column. In addition, default values for the turbulent diffusion of entrained air and dissolved oxygen have been updated.
The sharp-interface tracking Volume of Fluid (VOF) methods in FLOW-3D have seen improvements in both accuracy and robustness through the integration of fluid particles. This innovative approach introduces a new type of particle, referred to as VOF particles, which replaces the traditional VOF function for monitoring small fluid ligaments and droplets within the computational domain. As a result, this method enhances the conservation of fluid volume and momentum.
Related products
-

PointFuse Pro full cracked license
$ 200.00 Add to cart Quick View -

PhoToPlan Ultimate cracked version
$ 160.00 Add to cart Quick View -

Vertex G5 Mechanical 2018 v25.0.XX
$ 200.00 Add to cart Quick View -

CarMaker version 12 cracked license release
$ 200.00 Add to cart Quick View -

PointSense Total Package cracked version
$ 200.00 Add to cart Quick View -

ATOS Professional v7.5 – 3D Scanning and Inspection Software
$ 200.00 Add to cart Quick View -

FLOW-3D 2022R2 cracked license
$ 150.00 Add to cart Quick View -

CGG InsightEarth 3.7 cracked release
$ 160.00 Add to cart Quick View -
Sale!

Aspire Version 8.5 license software
$ 1,995.00Original price was: $ 1,995.00.$ 150.00Current price is: $ 150.00. Add to cart Quick View -

Trimble Inpho 9.1 cracked license
$ 140.00 Add to cart Quick View