Zemax OPTICSTUDIO 2024 R1 Enterprise cracked release
$ 160.00
Ansys Zemax OpticStudio is a comprehensive optical design software used for the design and analysis of a wide range of optical systems
Get everything you need to simulate, optimize, and tolerance your optical designs. Design complex optical systems for a wide range of applications with advanced features, including structural and thermal analysis.
Description
What’s New :
With the 2024 R1 release, Ansys Zemax OpticStudio delivers a comprehensive suite of features enhancing the support for multiphysics simulation, the design for manufacturing real optical systems, and enhanced support for incorporating diffractive optics.
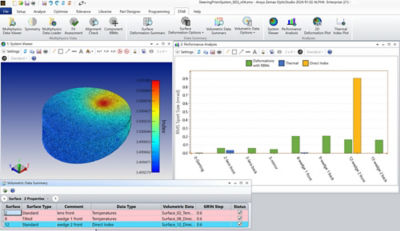
Expanded OpticStudio Workflow Capability
Enables you to use Ansys Zemax OpticStudio as part of your Ansys Multiphysics workflow. Load refractive index datasets from a wide range of sources, including computational fluid dynamics tools like Ansys Fluent.
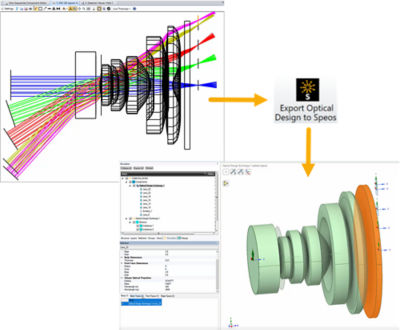
Enhanced Straylight Analysis
New workflow for import of lens geometries and optical properties from Ansys Zemax OpticStudio into Ansys Speos, compatible with the physical camera sensor. Streamlined and comprehensive straylight analysis in optical systems, including both free- floating lenses and constrained/housed lens systems, completed with the physical camera sensor.
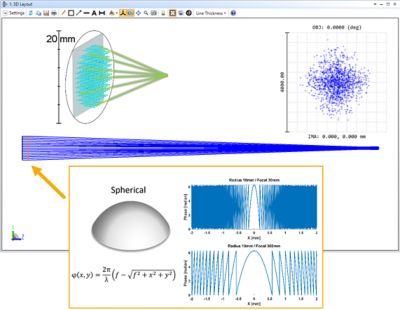
Metalens Simulation Advancements
New metalens simulation and analysis capabilities in Ansys Zemax OpticStudio: MTF, PSF, multi-scale, and multi-lens/metalens systems, new operands for phase constraint optimization. Simulate whole metalens with HPC CPU cluster, or accelerate FDTD with GPU (FDTD express mode).
Get everything you need to simulate, optimize, and tolerance your optical designs
Ansys Zemax OpticStudio is the solution for designing components and subassemblies within complex, high-precision optical systems. Such systems address a variety of applications across several high-growth industries, from AR/VR to LIDAR, medical imaging to data communications, and more.
Key Features
- Ray Tracing
- Lens Design
- Tolerance Analysis
- Optimization
- Interoperability
- Multiphysics Simulation
- User-friendly interface
A user-friendly interface with a wide range of tools, wizards, and visualizations to assist engineers in the design and analysis process.
OpticStudio 24.1 Release Notes
1 Tools, Features, and Capabilities
1.1 Offline legacy license activation (All Editions)
Activate, update, and transfer all your licenses offline.
A new Zemax License Manager release is included with OpticStudio or available as a separate download. This release adds an offline section with a built-in offline softkey license activation and license transfer process.
This means these operations no longer need to be done via a separate application. Since we are now issuing Ansys licenses, this also prepares Zemax legacy applications for the future discontinuation of the legacy online license servers.
2 Libraries and Catalogs
2.1 Catalog Updates (All Editions)
Get the latest material catalogs from Schott, Auer Lighting, CDGM, Heraeus, and Optimax.
Material Catalogs
Schott:
Preferred glasses updated with mechanical data.
New glasses added: F2HTi, FK5HTi, LF5HTi, LLF1HTi, N-BK7HTi, N-LAK28, N-LASF55, N-SF57HTultra, N-SF6HTultra, N-SF6Q2, N-SK5HTi, SF57HTultra, SF6HT, REALVIEW_1.9_LIGHTWEIGHT, and REALVIEW_2.0.
Auer Lighting:
SUPRAX updated with mechanical data.
CDGM:
Glasses updated with mechanical data.
New glasses added: H-FK55, H-ZLaF75C, H-ZLaF89LA, H-ZLaF96, D-ZK2A, D-ZK3A, and ZF7LT.
Heraeus:
Updated with mechanical data: HOMOSIL101_HERASIL102, HOQ_310, INFRASIL_301_302, SPECTROSIL_2000, SUPRASIL_1_2A, SUPRASIL_2B_CG, and SUPRASIL_300_3001_3002.
New glasses added: SUPRASIL_3301_3302 and SUPRASIL_311_312_313.
Optimax:
Updated with mechanical data: N-FK51A, N-PK51, S-BAH10, S-BAL14, S-BAL35, S-BSL7, S-BSM2, S-FPL51, S-FSL5, S-LAH51, S-LAH53, S-LAH58, S-LAH64, S-LAL8, S-LAL9, S-LAL54, S-LAM2, S-LAM7, S-NPH2, S-TIH1, S-TIH4, S-TIH6, S-TIH11, S-TIH53, S-TIL1, S-TIL6, S-TIL25, S-TIM2, S-TIM5, S-TIM22, S-TIM25, and S-TIM28.
New glasses added: N-K5 and N-SK4.
3 Bug Fixes
Diffraction Encircled Energy – Fixed an issue where incorrect reference coordinates were reported in Diffraction Encircled Energy if “Show Diffraction Limit” was not selected.
Parasolid CAD files – Fixed an issue where rays were not included in exported CAD files when using the Parasolid libraries.
Extended Diffraction Image Analysis – Fixed an issue for Extended Diffraction Image Analysis to improve results when paraxial and real image height calculations are significantly different.
Extended Diffraction Image Analysis – Fixed an issue in Extended Diffraction Image Analysis where the vertical image direction was inverted.
Exporting CAD files using Parasolid – Fixed a crash when exporting a CAD file using Parasolid when the system dimensions exceeded the maximum limits allowed by the Parasolid modelling kernel.
User Defined Surface – Fixed an issue with the files us_polarization2.cpp and us_polarization2.dll to correctly pass back reflection and transmission values when method 0 is selected.
Tolerance Operands – Fixed an issue where tolerance operands TRLX, TRLY, TRLR, TARX, TARY, and TARR could produce incorrect perturbation values of zero for non-axially symmetric systems.
Convert to NSC Group – Fixed an issue where an off-axis mirror with a floating aperture was not correctly converted during a sequential to non-sequential conversion.
Convert to NSC Group – Fixed an issue where a coating on a sequential mirror was applied to the wrong face after a sequential to non-sequential conversion
Black Box – Fixed multiple issues where certain systems with Black Box surfaces would not successfully export a Speos reduced order model.
Multiphysics Data Loader – Fixed a crash that could happen when loading STAR data for systems with Robust Ray Aiming turned on.
Convert ZRD or ZBF to TSV – Fixed an issue with the Convert ZRD or ZBF to TSV tool where it would fail to generate an output file when the ZRD file is too large.
SSAG MFE Operand – This fix enables calculation of the sag with no lateral limitations for cases where surface aperture is set to “None” or “Floating”. Typically, SSAG returns zero outside of the surface aperture.